14 Script Python Tự Động Hóa Thực Tế Cho Công Việc
Với 5 năm kinh nghiệm lập trình, tôi xin chia sẻ những script tự động hóa Python mà tôi thực sự đang sử dụng trong công việc! Thật lãng phí khi dành thời gian cho những công việc đơn điệu. Trong bài viết này, tôi đã chọn lọc những script Python thực sự hữu ích, từ xử lý dữ liệu đến giám sát hiệu suất.
Khi còn là kỹ sư mới vào nghề, tôi đã từng cảm thấy bực bội khi phải lặp đi lặp lại cùng một công việc. Chính lúc đó, tôi được đồng nghiệp cấp cao chỉ dạy về "sức mạnh của tự động hóa". Lần này, dựa trên kinh nghiệm đó, tôi sẽ chia sẻ những script giúp tăng hiệu quả công việc của bạn!
Công Cụ Xử Lý Dữ Liệu
1.1 Làm Sạch Dữ Liệu
Script này giúp loại bỏ các ô trống và dữ liệu trùng lặp trong file CSV chỉ với một thao tác. Tôi sử dụng nó mỗi khi tiền xử lý dữ liệu!
import pandas as pd
def clean_data(input_file, output_file):
df = pd.read_csv(input_file)
df.dropna(inplace=True) # Xóa giá trị trống
df.drop_duplicates(inplace=True) # Xóa giá trị trùng lặp
df.to_csv(output_file, index=False)
# Ví dụ sử dụng
clean_data("data.csv", "cleaned_data.csv")
1.2 So Sánh Dữ Liệu
Dễ dàng tìm ra sự khác biệt giữa hai file CSV. Rất hữu ích cho quản lý phiên bản và xác thực dữ liệu!
import pandas as pd
def compare_data(file1, file2):
df1 = pd.read_csv(file1)
df2 = pd.read_csv(file2)
diff = df1.compare(df2)
return diff
# Ví dụ sử dụng
result = compare_data("file1.csv", "file2.csv")
print(result)
Công Cụ Kiểm Tra Mạng
2.1 Kiểm Tra Cổng Mở
Script kiểm tra xem cổng của máy chủ có đang mở hay không. Tôi sử dụng nó như bước đầu tiên khi khắc phục sự cố!
import socket
def check_port(host, port):
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
result = sock.connect_ex((host, port))
sock.close()
return result == 0
# Ví dụ sử dụng
if check_port("example.com", 80):
print("Cổng 80 đang mở")
else:
print("Cổng 80 đang đóng")
2.2 Kiểm Tra Ping Hàng Loạt
Có thể thực hiện kiểm tra Ping cho nhiều máy chủ cùng một lúc. Lý tưởng cho việc phân tích sự cố mạng!
import os
def ping_hosts(hosts):
for host in hosts:
response = os.system(f"ping -c 1 {host}")
if response == 0:
print(f"{host} có phản hồi")
else:
print(f"{host} không có phản hồi")
# Ví dụ sử dụng
hosts = ["google.com", "example.com", "localhost"]
ping_hosts(hosts)
Công Cụ Tự Động Hóa Tác Vụ Hệ Thống
3.1 Giám Sát Dung Lượng Ổ Đĩa
Script cảnh báo khi dung lượng ổ đĩa còn ít. Đây là trợ thủ đắc lực cho quản trị viên máy chủ!
import shutil
def check_disk_space(path, threshold):
total, used, free = shutil.disk_usage(path)
free_gb = free // (2**30)
if free_gb < threshold:
print(f"Cảnh báo: Dung lượng trống dưới {threshold}GB.")
else:
print(f"Dung lượng trống: {free_gb}GB")
# Ví dụ sử dụng
check_disk_space('/', 10)
Công Cụ Tự Động Hóa Kiểm Thử
4.1 Kiểm Thử Đơn Vị Với unittest
Kiểm thử đơn vị để duy trì chất lượng mã. Đây là kỹ năng thiết yếu trong phát triển nhóm!
import unittest
def add(a, b):
return a + b
class TestMyFunction(unittest.TestCase):
def test_addition(self):
result = add(1, 2)
self.assertEqual(result, 3)
# Ví dụ sử dụng
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
Công Cụ Tự Động Hóa Quản Lý Tệp
5.1 Sắp Xếp Tệp Theo Phần Mở Rộng
Script "thần kỳ" giúp sắp xếp các tệp trong thư mục theo phần mở rộng. Lý tưởng cho việc sắp xếp máy tính!
import os
from shutil import move
def sort_files(directory_path):
for filename in os.listdir(directory_path):
file_path = os.path.join(directory_path, filename)
if os.path.isfile(file_path):
file_extension = filename.split('.')[-1]
destination_directory = os.path.join(directory_path, file_extension)
if not os.path.exists(destination_directory):
os.makedirs(destination_directory)
move(file_path, os.path.join(destination_directory, filename))
# Ví dụ sử dụng
sort_files('/path/to/directory')
5.2 Xóa Thư Mục Trống
Có thể xóa hàng loạt thư mục trống không cần thiết. Giúp ích cho việc sắp xếp hệ thống!
import os
def remove_empty_folders(directory_path):
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory_path, topdown=False):
for folder in dirs:
folder_path = os.path.join(root, folder)
if not os.listdir(folder_path):
os.rmdir(folder_path)
# Ví dụ sử dụng
remove_empty_folders('/path/to/directory')
5.3 Đổi Tên Hàng Loạt
Có thể đổi tên hàng loạt tệp cùng một lúc. Rất hữu ích cho việc sắp xếp ảnh hoặc quản lý tài liệu!
import os
def batch_rename(directory, prefix):
for count, filename in enumerate(os.listdir(directory)):
new_name = f"{prefix}_{count}.txt"
os.rename(os.path.join(directory, filename), os.path.join(directory, new_name))
# Ví dụ sử dụng
batch_rename("/path/to/files", "file")
5.4 Tìm Kiếm Tệp Lớn
Tìm ra các tệp lớn chiếm dụng dung lượng ổ đĩa. Trợ thủ đắc lực cho việc quản lý lưu trữ!
import os
def find_large_files(directory, size_limit_mb):
size_limit = size_limit_mb * 1024 * 1024 # Chuyển đổi sang byte
large_files = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(directory):
for file in files:
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
if os.path.getsize(file_path) > size_limit:
large_files.append(file_path)
return large_files
# Ví dụ sử dụng
large_files = find_large_files("/path/to/directory", 100) # Tìm tệp lớn hơn 100MB
print(large_files)
Công Cụ Giám Sát Hiệu Suất
6.1 Giám Sát Sử Dụng CPU và Bộ Nhớ
Có thể giám sát tình trạng sử dụng tài nguyên hệ thống theo thời gian thực. Thiết yếu cho việc tinh chỉnh hiệu suất!
import psutil
import time
def monitor_system(interval=1):
try:
while True:
cpu_usage = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=interval)
memory_usage = psutil.virtual_memory().percent
print(f"Sử dụng CPU: {cpu_usage}% | Sử dụng bộ nhớ: {memory_usage}%")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Đã dừng giám sát.")
# Ví dụ sử dụng
monitor_system(interval=2)
6.2 Giám Sát Sử Dụng GPU
Giám sát tình trạng sử dụng GPU, quan trọng trong học máy và phát triển game. Hữu ích cho việc tối ưu hóa tài nguyên!
import pynvml
def monitor_gpu_usage():
pynvml.nvmlInit()
device_count = pynvml.nvmlDeviceGetCount()
for i in range(device_count):
handle = pynvml.nvmlDeviceGetHandleByIndex(i)
util = pynvml.nvmlDeviceGetUtilizationRates(handle)
memory_info = pynvml.nvmlDeviceGetMemoryInfo(handle)
print(f"GPU {i}: Sử dụng={util.gpu}%, Bộ nhớ sử dụng={memory_info.used / 1024 ** 2} MB")
# Ví dụ sử dụng
monitor_gpu_usage()
6.3 Giám Sát Băng Thông Mạng
Có thể giám sát tình trạng sử dụng mạng theo thời gian thực. Hữu ích cho việc xác định nguyên nhân sự cố truyền thông!
import psutil
import time
def monitor_network_usage(interval=1):
old_value = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent + psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv
try:
while True:
new_value = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent + psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv
bandwidth = (new_value - old_value) / interval # byte/giây
print(f"Băng thông mạng: {bandwidth} B/s")
old_value = new_value
time.sleep(interval)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Đã dừng giám sát.")
# Ví dụ sử dụng
monitor_network_usage(interval=2)
6.4 Giám Sát I/O Ổ Đĩa
Giám sát tốc độ đọc/ghi ổ đĩa. Lý tưởng cho việc xác định điểm nghẽn lưu trữ!
import psutil
import time
def monitor_disk_io(interval=1):
old_read = psutil.disk_io_counters().read_bytes
old_write = psutil.disk_io_counters().write_bytes
try:
while True:
new_read = psutil.disk_io_counters().read_bytes
new_write = psutil.disk_io_counters().write_bytes
read_speed = (new_read - old_read) / interval
write_speed = (new_write - old_write) / interval
print(f"Tốc độ đọc: {read_speed / 1024} KB/s | Tốc độ ghi: {write_speed / 1024} KB/s")
old_read = new_read
old_write = new_write
time.sleep(interval)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Đã dừng giám sát.")
# Ví dụ sử dụng
monitor_disk_io(interval=2)
6.5 Giám Sát Sử Dụng Tài Nguyên Tiến Trình
Giám sát tình trạng sử dụng tài nguyên của một tiến trình cụ thể. Hữu ích cho việc phân tích hiệu suất ứng dụng!
import psutil
def monitor_process(pid):
process = psutil.Process(pid)
try:
while True:
cpu_usage = process.cpu_percent(interval=1)
memory_usage = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 ** 2 # Chuyển đổi sang MB
print(f"PID {pid}: CPU={cpu_usage}%, Bộ nhớ={memory_usage} MB")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Đã dừng giám sát.")
# Ví dụ sử dụng
monitor_process(1234) # Thay thế bằng PID của tiến trình mục tiêu
Công Cụ Phân Tích Nhật Ký
7.1 Thống Kê Lỗi Tần Suất Cao Trong Nhật Ký
Trích xuất và tổng hợp các lỗi thường xuyên xuất hiện từ tệp nhật ký. Hữu ích cho việc xác định nguyên nhân gốc rễ của vấn đề!
from collections import Counter
import re
def top_n_errors(log_file, n=5):
error_pattern = re.compile(r"ERROR: (.+)")
errors = []
with open(log_file, 'r') as f:
for line in f:
match = error_pattern.search(line)
if match:
errors.append(match.group(1))
return Counter(errors).most_common(n)
# Ví dụ sử dụng
top_errors = top_n_errors("app.log", n=3)
print(top_errors)
7.2 Lọc Nhật Ký Theo Khoảng Thời Gian
Có thể trích xuất nhật ký chỉ trong một khoảng thời gian cụ thể. Lý tưởng cho việc phân tích tình huống khi xảy ra sự cố!
from datetime import datetime
def filter_logs_by_time(log_file, start_time, end_time, output_file):
start = datetime.strptime(start_time, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
end = datetime.strptime(end_time, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
with open(log_file, 'r') as f:
logs = f.readlines()
filtered_logs = []
for log in logs:
log_time_str = log.split()[0] + " " + log.split()[1] # Giả định dấu thời gian là hai phần đầu tiên của nhật ký
log_time = datetime.strptime(log_time_str, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
if start <= log_time <= end:
filtered_logs.append(log)
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
f.writelines(filtered_logs)
# Ví dụ sử dụng
filter_logs_by_time("app.log", "2025-02-26 12:00:00", "2025-02-26 14:00:00", "filtered_logs.log")
7.3 Trích Xuất Thông Tin Lỗi Từ Nhật Ký
Trích xuất chỉ thông tin lỗi từ tệp nhật ký. Giúp tiết kiệm thời gian khắc phục sự cố!
def extract_errors(log_file, output_file):
with open(log_file, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
errors = [line for line in lines if "ERROR" in line]
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
f.writelines(errors)
# Ví dụ sử dụng
extract_errors("app.log", "errors.log")
7.4 Gộp Tệp Nhật Ký
Gộp nhiều tệp nhật ký thành một. Hữu ích cho việc phân tích hệ thống phân tán!
def merge_log_files(log_files, output_file):
with open(output_file, 'w') as outfile:
for log_file in log_files:
with open(log_file, 'r') as infile:
outfile.write(infile.read())
# Ví dụ sử dụng
merge_log_files(["log1.log", "log2.log", "log3.log"], "merged_logs.log")
7.5 Giám Sát Tệp Nhật Ký Theo Thời Gian Thực
Giám sát cập nhật tệp nhật ký theo thời gian thực. Hữu ích cho việc phản ứng ngay lập tức khi xảy ra sự cố!
import time
def tail_log_file(log_file):
with open(log_file, 'r') as f:
f.seek(0, 2) # Di chuyển đến cuối tệp
try:
while True:
line = f.readline()
if line:
print(line.strip())
else:
time.sleep(0.1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Đã dừng giám sát.")
# Ví dụ sử dụng
tail_log_file("app.log")
Công Cụ Tự Động Hóa Email
8.1 Gửi Email Cá Nhân Hóa (Lưu ý bảo mật: Không nên mã hóa cứng mật khẩu)
Có thể gửi email được cá nhân hóa cho nhiều người nhận. Hữu ích cho việc tự động hóa phản hồi khách hàng hoặc thông báo!
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart
def send_personalized_email(sender_email, sender_password, recipients, subject, body):
server = smtplib.SMTP('smtp.gmail.com', 587)
server.starttls()
server.login(sender_email, sender_password)
for recipient_email in recipients:
message = MIMEMultipart()
message['From'] = sender_email
message['To'] = recipient_email
message['Subject'] = subject
message.attach(MIMEText(body, 'plain'))
server.send_message(message)
server.quit()
# Ví dụ sử dụng
sender_email = 'your_email@gmail.com'
sender_password = 'your_password' # Khuyến nghị sử dụng mật khẩu ứng dụng
recipients = ['recipient1@example.com', 'recipient2@example.com']
subject = 'Xin chào'
body = 'Đây là email kiểm tra.'
send_personalized_email(sender_email, sender_password, recipients, subject, body)
Công Cụ Thao Tác Cơ Sở Dữ Liệu
9.1 Kết Nối Đến Cơ Sở Dữ Liệu SQLite
Kết nối đến cơ sở dữ liệu SQLite và thực thi truy vấn. Lý tưởng cho việc quản lý dữ liệu của ứng dụng nhỏ!
import sqlite3
def connect_to_database(db_path):
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
return conn, cursor
def execute_query(cursor, query):
cursor.execute(query)
results = cursor.fetchall()
return results
# Ví dụ sử dụng
conn, cursor = connect_to_database('/path/to/database.db')
query = 'SELECT * FROM table_name'
results = execute_query(cursor, query)
print(results)
conn.close()
Nhận Dạng OCR
10.1 Nhận Dạng Văn Bản Từ Hình Ảnh
Trích xuất văn bản từ hình ảnh. Hữu ích cho việc số hóa tài liệu hoặc tự động hóa trích xuất thông tin!
import pytesseract
from PIL import Image
def recognize_text(image_path):
image = Image.open(image_path)
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(image, lang='vie') # Sử dụng tiếng Việt
return text
# Ví dụ sử dụng
text = recognize_text('/path/to/image.jpg')
print(text)
Tự Động Hóa Thao Tác PDF
11.1 Trích Xuất Văn Bản Từ PDF
Trích xuất văn bản từ tệp PDF. Giúp nâng cao hiệu quả xử lý tài liệu!
import PyPDF2
def extract_text_from_pdf(pdf_path):
with open(pdf_path, 'rb') as file:
reader = PyPDF2.PdfReader(file)
text = ''
for page in reader.pages:
text += page.extract_text() or ''
return text
# Ví dụ sử dụng
text = extract_text_from_pdf('/path/to/document.pdf')
print(text)
Tự Động Hóa Thu Thập Dữ Liệu Web
12.1 Trích Xuất Dữ Liệu Từ Trang Web
Trích xuất thông tin từ trang web. Hữu ích cho việc tự động hóa nghiên cứu thị trường hoặc thu thập thông tin!
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
def scrape_data(url):
response = requests.get(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
return soup
# Ví dụ sử dụng
url = 'https://example.com'
soup = scrape_data(url)
print(soup.title.string)
12.2 Tải Hình Ảnh Hàng Loạt
Tải xuống hàng loạt hình ảnh từ web. Giúp tiết kiệm thời gian thu thập tài liệu!
import requests
import os
def download_images(url, save_directory):
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
images = response.json() # Giả định API trả về mảng JSON của URL hình ảnh
for index, image_url in enumerate(images):
image_response = requests.get(image_url)
if image_response.status_code == 200:
with open(os.path.join(save_directory, f"image_{index}.jpg"), "wb") as f:
f.write(image_response.content)
# Ví dụ sử dụng
download_images('https://api.example.com/images', '/path/to/save')
Tự Động Hóa Excel
13.1 Đọc và Ghi Excel
Tự động hóa việc đọc và ghi tệp Excel. Rất hữu ích cho việc nâng cao hiệu quả công việc văn phòng!
import pandas as pd
def read_excel(file_path):
df = pd.read_excel(file_path)
return df
def write_to_excel(data, file_path):
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.to_excel(file_path, index=False)
# Ví dụ sử dụng
data = {'Cột1': [1, 2, 3], 'Cột2': [4, 5, 6]}
write_to_excel(data, '/path/to/output.xlsx')
df = read_excel('/path/to/output.xlsx')
print(df)
Tự Động Hóa Chỉnh Sửa Hình Ảnh
14.1 Thay Đổi Kích Thước Hình Ảnh
Có thể thay đổi kích thước hàng loạt hình ảnh. Hữu ích cho việc tối ưu hóa hình ảnh cho web!
from PIL import Image
def resize_image(input_path, output_path, width, height):
image = Image.open(input_path)
resized_image = image.resize((width, height), Image.LANCZOS)
resized_image.save(output_path)
# Ví dụ sử dụng
resize_image('/path/to/input.jpg', '/path/to/output.jpg', 800, 600)
Sau Script Là Gì? Cách Phát Triển Hiệu Quả Hơn
14 script Python đã giới thiệu ở trên đã có thể giúp công việc hàng ngày của bạn trở nên dễ dàng hơn nhiều.
Tuy nhiên, trong môi trường phát triển thực tế, bạn có thể có nhu cầu như "kiểm thử API liên tục" hoặc "chia sẻ thông số kỹ thuật trong nhóm". 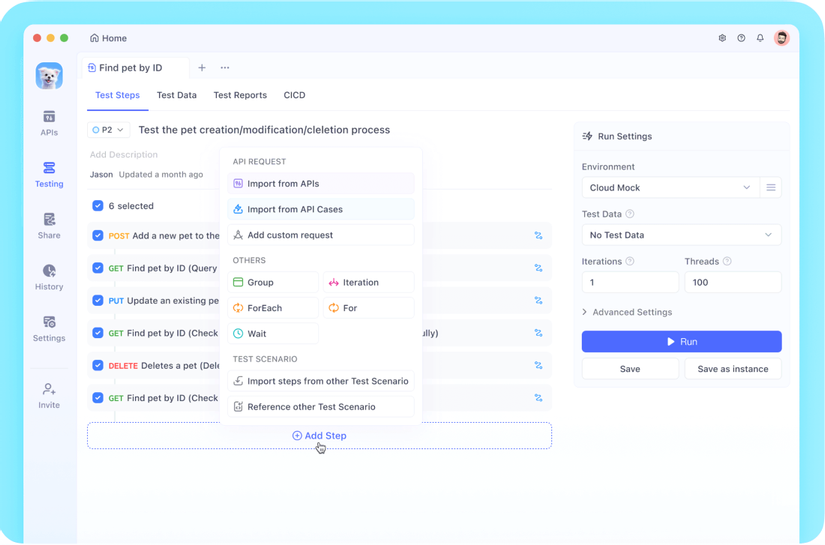
Trong trường hợp đó, tôi khuyên bạn nên thử Apidog. Từ thiết kế API, mô phỏng, kiểm thử đến quản lý tài liệu, tất cả đều có thể được thực hiện trên một nền tảng, giúp làm việc hiệu quả hơn so với các script.
Bạn có thể xem việc tự động hóa bằng script Python là bước đầu tiên, và thử Apidog như bước tiếp theo.
Tóm Tắt
14 script mà tôi đã giới thiệu đều là những script mà tôi thực sự sử dụng trong công việc hàng ngày. Bắt đầu từ những tự động hóa nhỏ và dần dần tự động hóa cả những tác vụ phức tạp, tôi đã có thể tập trung vào những công việc thực sự có giá trị.
Hãy xem xét công việc của bạn và nếu bạn nhận ra "Mình đang làm cùng một việc lặp đi lặp lại", hãy cân nhắc tự động hóa. Tôi tin rằng giá trị thực sự của lập trình là giải phóng con người khỏi những công việc nhàm chán!
Tôi hy vọng bài viết này sẽ giúp nâng cao hiệu quả công việc của bạn. Nếu bạn có câu hỏi hoặc script tự động hóa yêu thích của riêng mình, hãy chia sẻ trong phần bình luận!
All Rights Reserved